Positive Displacement Pumps
A Positive Displacement pump is also known as the power pump and it operates by continuously deliver liquid flow but independent of the pressure in the discharge piping system. The discharge piping system produces resistance to this liquid flow, thereby generating pressure in the discharge piping system. Unlike centrifugal pump, it does not develop pressure but rather produces a flow of liquid.
Positive Displacement pumps can be further divided based on the mode of displacement:
- Reciprocating Pumps – works in a transitory dynamic condition called the pumping cycle via linear movement of the plunger or piston. A reciprocating pump makes up of liquid end and power end.
- Rotary Pumps – the displacement is by rotating action of gears, screws or vanes in a fixed casing/ chamber. Rotary pumps do not generate pulsation. The inherent high efficiency of a rotary pump makes its design very suitable to handle high viscosity liquid.
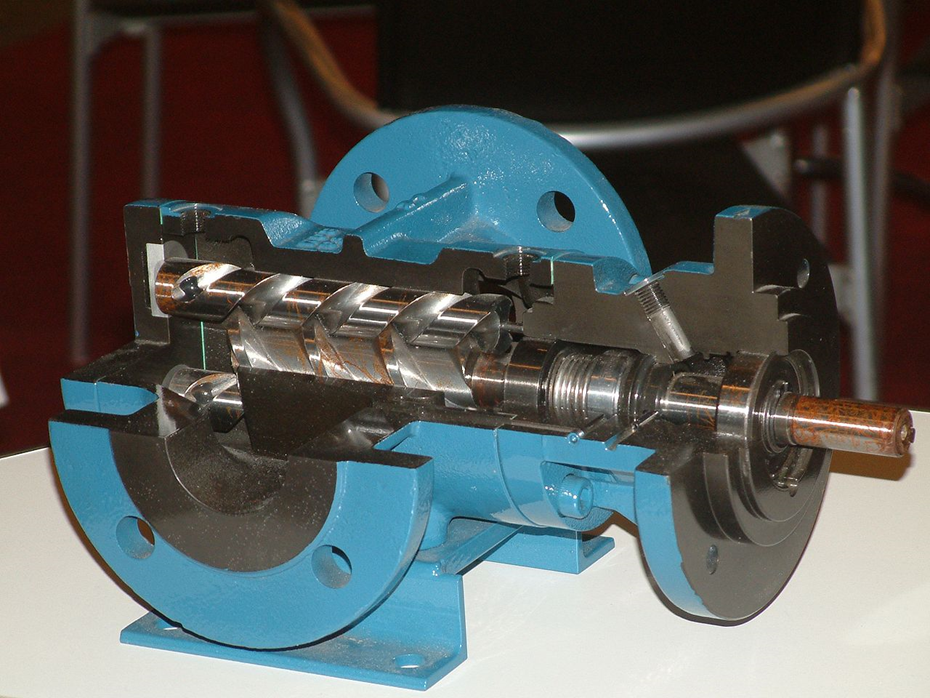
Figure 2. Screw Pump Cutout (Credit to CC BY-SA)
Dynamic Pumps
A Dynamic pump is distinguished by the way it operates. It uses a centrifugal force of the rotating impeller to impart kinetic energy to the fluid, moving the fluid from one level of pressure to a higher level of pressure.
There are several varieties of dynamic pumps and some are classified as follow:
- Centrifugal Pumps are the most widely used fluid handling devices in the refining, petrochemical and general industrial applications. Typically, more than 85% of the pumps installed in an industry are centrifugal pumps.
- Regenerative Pumps are also sometimes called peripheral pumps. This type of pumps in general produces high head and low flow. It can also handle a certain amount of air or gas in the liquid as long as sufficient liquid remains in the pump casing to seal the clearance between the suction and discharge passages.
- Vortex Pumps or recess impeller pumps are designed to handle liquid with solids without clogging the casing passage.
- Special Effect Pumps are particularly used for specialized conditions in an industrial service.
